23.08.04. 풀었던 문제들 복기
Leetcode 139. Word Break, 1시간
첫 접근
처음에는 일단 brute-force로 접근했다. for문으로는 돌릴 수 없어서, dfs를 사용한 backtracking으로 접근했다. 코드는 뭐.. 간단하다. DFS(i)는 i부터 s.length()까지 만들 수 있는지 여부이다. 내부적인 구현은, i부터 모든 wordDict를 순회하면서 끝까지 도달할 수 있으면 true, 아니면 false인 식으로
class Solution {
public:
bool DFS(int i, string& s, vector<string>& wordDict){
if(i == s.length()) return true;
for(string word : wordDict){
int wordlen = word.length();
if(s.substr(i, wordlen) == word){
bool result = DFS(i + wordlen, s, wordDict);
if(result) return result;
}
}
return false;
}
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
return DFS(0, s, wordDict);
}
};TLE 난다.
두 번째 접근
TLE가 나는 이유 중 하나는 탐색했던 것을 또 탐색하기 때문이다. 예를 들어 DFS(10)을 이미 탐색했는데 또 탐색하는 일이 발생하기 때문에, DP를 사용하면 해결된다.
이미 탐색한 내용이라면 그 값을 돌려주게 설정하고, 새로운 탐색이 이뤄지면 그 값을 저장하게 한다. 생각보다 별 것 없는 DP.
// Runtime 2 ms Beats 91.83%
// Memory 7.7 MB Beats 85.40%
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dp;
bool DFS(int i, string& s, vector<string>& wordDict){
if(i == s.length()) return true;
if(dp[i] != -1) return dp[i];
for(string word : wordDict){
int wordlen = word.length();
if(s.substr(i, wordlen) == word){
bool result = DFS(i + wordlen, s, wordDict);
dp[i] = result;
if(result) return result;
}
}
dp[i] = false;
return false;
}
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
dp.resize(s.length());
fill(dp.begin(), dp.end(), -1);
return DFS(0, s, wordDict);
}
};
/*
dp[i] : i부터 끝까지 봤을 때 만들 수 있는지
*/
후기
생각보다 별 것 없는 DP이지만, + 첫 접근도 잘 했지만 DP는 너무 어렵다.
BOJ 1543. 문서 검색, 6분
string의 find 함수와 getline만 알고 있다면 벌 이상없이 쉽게 풀리는 문제. find() 함수를 잘 써 보자.
void solve(){
string doc, s;
getline(cin, doc);
getline(cin, s);
int answer = 0, idx = 0;
while(1){
int nth_idx = doc.find(s, idx);
if(nth_idx == string::npos) break;
answer++;
idx = nth_idx+s.length();
}
cout<<answer;
}
BOJ 28419. 더하기, 10분
직관으로 풀 수 있는 문제. 단, 범위를 유의해야 했다.
짝수 합, 홀수 합으로 나누고,
- even sum에 2를 더하고 odd sum에 1 더하거나
- even sum에 1 더하고 odd sum에 2 더하거나
위 2개의 operation을 수행할 수 있다. 따라서 even sum - odd sum의 절댓값을 리턴하면 된다.
단, N == 3인 경우 위의 operation만 수행할 수 있으므로 evensum이 더 크다면 -1.
ll solve(){
int n; cin>>n;
ll oddsum = 0, evensum = 0;
int input;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
cin>>input;
if(i % 2 == 0) evensum += input;
else oddsum += input;
}
if(oddsum == evensum) return 0;
if(n == 3 && evensum > oddsum) return -1;
return abs(evensum - oddsum);
// 연산은 총 2가지.
// evensum에 2 더하고 oddsum에 1 더하거나
// evensum에 1 더하고 oddsum에 2 더하거나.
// N == 3인 경우는 1번밖에 못함. -> evensum이 더 큰 경우 불가능.
}
BOJ 21773. 가희와 프로세스, 30분
문제가 던져주는 대로 구현하면 되는 문제. priority를 쓰니까, 당연히 priority queue를 써야 한다.
유의해야 할 점은, 진짜 주는 대로 구현하면, 각 연산이 O(nlogn)만큼의 시간을 쓰기 때문에 전체 시간이 O(Tnlogn)이 되어서 TLE가 난다. 떄문에 [현 작업을 제외한 나머지 priority를 증가시킨다]의 의미를 잘 생각해 봐야 한다.
현 작업의 priority를 1 감소시키는 것 == 다른 모든 작업의 priority를 1 증가시키는 것과 동일하다.
struct process{
int id, time, priority;
};
struct comp{
bool operator()(const process &a, const process &b){
if(a.priority == b.priority) return a.id > b.id;
return a.priority < b.priority;
}
};
void solve(){
int T, n; cin>>T>>n;
priority_queue<process, vector<process>, comp> pq;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
process p;
cin>>p.id>>p.time>>p.priority;
pq.push(p);
}
while(T--){
process p = pq.top(); pq.pop();
cout<<p.id<<'\n';
p.time--;
if(p.time == 0) continue;
p.priority--;
pq.push(p);
}
}
BOJ 6593. 상범 빌딩, 15분
정석 BFS 문제. BFS하듯 dr/dc/dl 쓰면 되고, q에 넣을 때 visited = true만 해 주면 된다. 그리고 좌표 기반이니까 다음 좌표로 넘어갈 때 seg fault 안 나게 검사해 주고, unvisited 검사하면 된다.
struct coord{
int l, r, c;
};
int dr[6] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0};
int dc[6] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0};
int dl[6] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, -1};
string solve(int L, int R, int C){
coord S, E;
vector<vector<vector<char>>> dimension(L, vector<vector<char>>(R, vector<char>(C)));
vector<vector<vector<bool>>> visited(L, vector<vector<bool>>(R, vector<bool>(C, false)));
for(int l = 0; l<L; l++){
for(int r = 0; r<R; r++){
for(int c = 0; c<C; c++){
cin>>dimension[l][r][c];
if(dimension[l][r][c] == 'S'){
S.l = l; S.r = r; S.c = c;
}
else if(dimension[l][r][c] == 'E'){
E.l = l; E.r = r; E.c = c;
}
}
}
}
queue<pair<coord, int>> q;
q.push({S, 0});
visited[S.l][S.r][S.c] = true;
while(!q.empty()){
coord f = q.front().first; int fmin = q.front().second; q.pop();
if(f.l == E.l && f.r == E.r && f.c == E.c){
return "Escaped in " + to_string(fmin) + " minute(s).";
}
for(int i = 0; i<6; i++){
int nl = f.l + dl[i];
int nr = f.r + dr[i];
int nc = f.c + dc[i];
if(0 <= nl && nl < L && 0 <= nr && nr < R && 0 <= nc && nc < C && dimension[nl][nr][nc] != '#' && !visited[nl][nr][nc]){
q.push({{nl, nr, nc}, fmin + 1});
visited[nl][nr][nc] = true;
}
}
}
return "Trapped!";
}
//////////////////////
int main(void) {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
int L, R, C;
while(1){
cin>>L>>R>>C;
if(L == 0 && R == 0 && C == 0) break;
cout<<solve(L, R, C)<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
BOJ 11576. base conversion, 6분
A진법을 10진법으로 바꿨다가 B진법으로 바꾸면 된다. 별 것 없는 문제.
void solve(){
int A, B; cin>>A>>B;
int m; cin>>m;
vector<int> digits(m);
for(int i = m-1; i>=0; i--) cin>>digits[i];
int ten = 0, mul = 1;
for(int digit : digits){
ten += digit * mul;
mul *= A;
}
vector<int> result;
while(ten){
result.push_back(ten % B);
ten /= B;
}
for(int i = result.size()-1; i>=0; i--) cout<<result[i]<<' ';
}
BOJ 4396. 지뢰 찾기, 25분
코드는 좀 길게 작성되었는데. 오타 몇 개 때문에 시간을 좀 보냈다.
int dr[8] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1};
int dc[8] = {1, 0, -1, 1, -1, 1, 0, -1};
void solve(){
int n; cin>>n;
vector<vector<bool>> isMine(n, vector<bool>(n, false)); // mine(*)이면 true, else false
vector<vector<int>> numMine(n, vector<int>(n, 0));
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){
char input; cin>>input;
if(input == '*'){
isMine[i][j] = true;
for(int d = 0; d<8; d++){
int nr = i + dr[d];
int nc = j + dc[d];
if(0 <= nr && nr < n && 0 <= nc && nc < n){
numMine[nr][nc]++;
}
}
}
}
}
bool isExplode = false;
vector<vector<bool>> isInput(n, vector<bool>(n, false)); // isInput(x)면 true, else false
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){
char input; cin>>input;
if(input == 'x'){
isInput[i][j] = true;
if(isMine[i][j]) isExplode = true;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(isExplode && isMine[i][j]) cout<<'*';
else if(isInput[i][j]) cout<<numMine[i][j];
else cout<<'.';
}
cout << '\n';
}
}
후기
solved.ac에서 랜덤 돌릴 때 *s..g !@$me로 [내가 풀지 않았던 실버~골드 문제]로 추출해서 푼다.
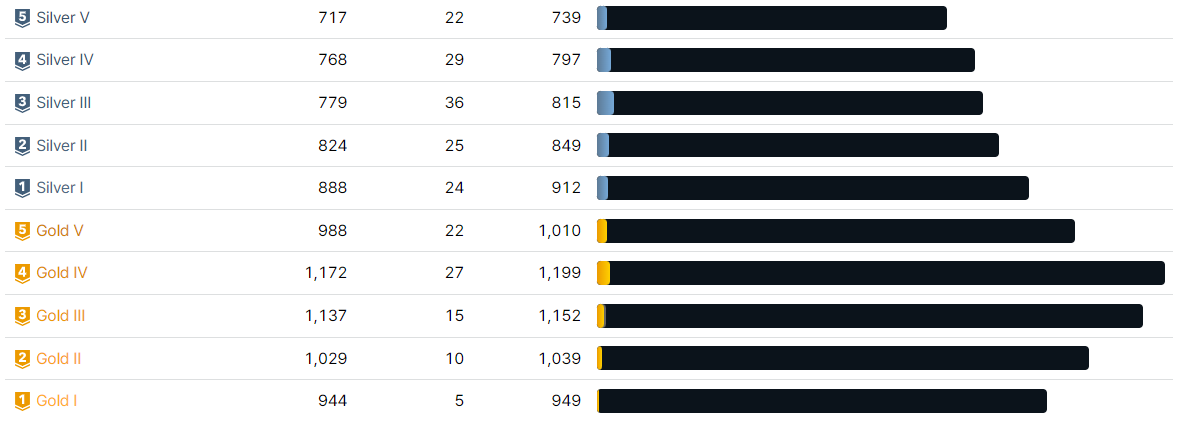
문제 비율은 골드가 훨씬 더 높은 것 같은데.. 영어 문제를 제해서 그런가? 실버 문제가 굉장히 많이 나오는 느낌이 든다.
가능하면, 실버 문제들은 정확하고, 빠르게 + 원큐에 풀 수 있도록 해 보자. 솔직히 문제를 잘못 풀어서 걸리는 overhead보다 문제를 정확하게 읽는 조금의 overhead가 훨씬 적으니까.