Codeforces #786 Div. 3
https://codeforces.com/contest/1674
Dashboard - Codeforces Round #786 (Div. 3) - Codeforces
codeforces.com
결과
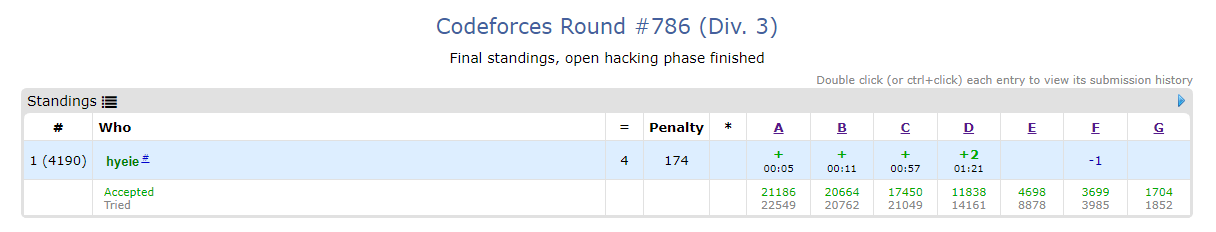
언제쯤 4/7의 벽을 통과할까. 그리고 C번 - 문제 이해를 잘못해서 뇌절을 좀 했다. D번도 직관으로 풀다가 틀려서 논리로 풀었고. 음.. 문제 풀 때, 완벽하게 증명된 경우에만 코드로 옮기는 걸 해야겠다.
A번
문제에 낚였다. 주어진 조건이 10^9를 초과하지 않는 a, b를 구하라길래 sqrt 쓸 준비 하고 있었는데, x와 y가 둘 다 100보다 작다. 즉슨, a는 무조건 1로 두고 b는 y/x로 두면 된다는 말이다....
ll STANDARD = 1000000000;
void solve(){
ll x, y; cin>>x>>y;
// a, b를 골라서 x를 a번 곱함 b^a * x = y가 되는 a, b를 구하라
if(y%x != 0){
cout<<"0 0\n";
return;
}
ll a = 1, b = y/x;
cout<<a<<' '<<b<<'\n';
}
B번
미리 dictionary를 만들고, 정렬한 다음 그 값을 찾으면 된다. 어렵진 않은 문제.
vector<string> bl;
void init(){
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++){
for (char cc = 'a'; cc <= 'z'; cc++){
string empty = "";
empty += c;
empty += cc;
if (c == cc)
continue;
else
bl.push_back(empty);
}
}
sort(bl.begin(), bl.end(), less<string>());
}
void solve(){
string s; cin>>s;
cout<<find(bl.begin(), bl.end(), s) - bl.begin() + 1 <<'\n';
}
C번
문제를 잘못 이해해서 많은 시간을 쓴 문제. s는 a로만 구성되어 있고, 문자열 t "전체"와 바꿀 수 있는 게 문제였는데 나는 t의 한 문자와 바꿀 수 있다고 이해했다. 그래서 대체 어떻게 풀지?를 고민했는데... 허무했다.
만약 t가 a인 경우에는 s가 바뀌지 않으므로 경우의 수 1개,
t가 길이가 2 이상이며, a를 포함하는 경우 INF개,
그렇지 않은 경우 2^(s.length())개이다. s의 각각의 a 하나마다 '바꿀지, 안바꿀지' 경우의 수가 2개이기 때문.
void solve(){
string s; cin>>s; // a로만 구성
string t; cin>>t; // lowercase, 50 이하
// t가 "a"인 경우 : 1개
// t가 "*a*"인 경우 : INF개
if(t == "a"){
cout<<"1\n";
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i<t.length(); i++){
if(t[i] == 'a'){
cout<<"-1\n";
return;
}
}
/*
a를 t와 바꾸는 것
2^(sl)
*/
ll cnt = 1, sl = s.length();
while(sl--){
cnt *= 2LL;
}
cout<<cnt<<'\n';
}
D번
직관으로는 맞게 풀었는데, 디테일에서 조금 오류가 났던 문제.
증명은 아래와 같다.

string yes = "YES\n", no="NO\n";
void swap(int& a, int& b){
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void solve(){
int n; cin>>n;
vector<int> arr(n);
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) cin>>arr[i];
// 풀이 1
/*
step 1 : a가 비지 않았으면 a.back()을 뽑아서 b의 middle에 넣음. b가 홀수길이면 b의 왼쪽 가운데, 또는 오른쪽 가운데 선택해서 올림
-> a.front()는 맨 마지막에 들어감
step 2 : b가 빌때까지 b의 middle을 골라서 c의 end에 넣음. b가 짝수길이면 뭘 골라도 상관없음
a가 짝수개 -> a[1], a[3]는 앞뒤 맘대로 넣을 수 있음
a가 홀수개 -> a[0], a[2]이 앞뒤 맘대로 들어감
*/
vector<int> c;
int type = arr.size() % 2;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
c.push_back(arr[i]);
if(c.size() % 2 == type && c.size() > type + 1){
if(c[c.size() - 2] > c[c.size()-1]){
swap(c[c.size() - 2], c[c.size() - 1]);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i<n; i++){
if(c[i-1] > c[i]){
cout<<no;
return;
}
}
cout<<yes;
// 풀이 2
/*
// a가 홀수면 [1, 2], [3, 4], ...를 교체 가능
// a가 짝수면 [0, 1], [2, 3], ...을 교체 가능
*/
int type = arr.size() % 2;
for(int i = type; i<n; i += 2){
if(arr[i] > arr[i+1]) swap(arr[i], arr[i+1]);
}
for(int i = 1; i<n; i++){
if(arr[i-1] > arr[i]){
cout<<no;
return;
}
}
cout<<yes;
}
Upsolving
E번
DP인줄 알았는데, 그냥 전수탐색 문제였다.
- 완전 별개의 2개 벽을 부수는 경우 type1
- 하나 부수는데 ceil(ai/2)
-> ceil(ai/2) + ceil(aj/2)
- 하나 부수는데 ceil(ai/2)
- 연속된 2개 벽을 부수는 경우 type2 - 유의해야 했었다.
- 한번 쏘는 데 평균적 3딜 줌(둘 다 있을 때)
하나 없으면 2딜 줌
-> 최대한 고루 때려야 함
-> ceil((ai+aj)/3) - 다만 고루 때려도 남는 경우. 2 * ai < aj와 같은 경우
-> aj만 때려도 ai 사라짐
-> ceil(aj/2)
- 한번 쏘는 데 평균적 3딜 줌(둘 다 있을 때)
- 사이에 1칸 있는 2개 벽을 부수는 경우 type3
가운데 쏘면 양쪽에 1씩, 한쪽에 쏘면 [2, 0]이 들어감. 평균적으로 2딜이 들어감.
-> ceil((ai + aj) / 2)
int n, INF = 1000000000;
vector<int> arr;
int type1(){
vector<int> nums(n);
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
nums[i] = (int)ceil((double)arr[i] / 2);
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), less<int>());
return nums[0] + nums[1];
}
int type2(){
int min_value = INF;
for(int i = 0; i<n-1; i++){
int x = arr[i], y = arr[i+1];
if(x > y){ // after swap, x <= y
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
if(2 * x < y){
min_value = min(min_value, (int)ceil((double)y / 2));
}
else{
min_value = min(min_value, (int)ceil((double)(x + y)/3));
}
}
return min_value;
}
int type3(){
int min_value = INF;
for(int i = 1; i<n-1; i++){
int x = arr[i-1], y = arr[i+1];
min_value = min(min_value, (int)ceil((double)(x+y)/2));
}
return min_value;
}
void solve(){
cin>>n;
arr.resize(n);
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) cin>>arr[i];
int result = INF;
int a = type1(), b = type2(), c = type3();
result = min(result, a);
result = min(result, b);
result = min(result, c);
cout<<result;
}
F번
처음에는 brute-force로 했는데, query가 20만개, board가 1000 * 1000이니까 이렇게 하면 안된다. 따라서, 각 query를 log(1000000)으로 처리하거나 O(1)에 처리할 수 있어야 한다. 풀이는 기가 막혔다.
먼저, 문제 조건에서 왼쪽부터 column을 채워가니까 구현의 편리를 위해 matrix를 column 순서대로 string을 만든다. 그러면 (r, c)는 r + c * (# of row)의 index로 바뀌게 된다.
다음으로, 전체 icon 개수를 num_icon이라 하고, index 0 ~ num_icon까지 empty 개수를 num_empty라고 하자.
- 만약 바꾸는 index가 num_icon보다 크거나 같다면(바깥쪽이라면)
- 원래 empty여서 icon을 추가해야 하는 경우
- 경계가 1칸 늘어날 것이고, 새로 추가된 것이 .이라면 num_empty++
- 이후 num_icon++
- 원래 icon이어서 empty로 바뀌는 경우
- 경계가 1칸 줄어들 것이고, 원래 있던 것이 .이었다면 num_empty--
- 이후 num_icon--
- 원래 empty여서 icon을 추가해야 하는 경우
- 바꾸는 index가 num_icon보다 작다면(안쪽이라면)
- 원래 empty여서 icon을 추가해야 하는 경우
- 경계가 1칸 늘어날 것이고, 새로 추가된 것이 .이라면 num_empty++
- 이후 num_icon++
- 원래 있던 empty가 사라졌으므로 num_empty--
- 원래 icon이어서 empty로 바뀌는 경우
- 경계가 1칸 줄어들 것이고, 원래 있던 것이 .이었다면 num_empty--
- 이후 num_icon--
- 원래 있던 icon이 empty로 되었으므로 num_empty++
- 원래 empty여서 icon을 추가해야 하는 경우
// * : icon, . : empty
void solve(){
int n, m, q; cin>>n>>m>>q;
vector<string> strs(n);
// desktop : 전체
int num_icons = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
cin>>strs[i];
for(int c= 0 ;c<m; c++){
if(strs[i][c] == '*') num_icons++;
}
}
string desktop = "";
for(int c = 0; c<m; c++){
for(int r = 0; r<n; r++){
desktop += (strs[r][c]);
}
}
int num_empty = 0; // 0부터 채워야 할 icon 개수까지 empty 개수
for(int i = 0; i<num_icons; i++){
if(desktop[i] == '.') num_empty++;
}
int xi, yi;
while(q--){
cin>>xi>>yi;
int index = (xi - 1) + (yi - 1) * n;
if(index >= num_icons){ // 바깥쪽인 경우
if(desktop[index] == '.'){
desktop[index] = '*'; // *이 늘어난 경우.
if(desktop[num_icons] == '.'){ // 추가될 것이 .이면 empty++
num_empty++;
}
num_icons++;
}
else{ // == '*'
desktop[index] = '.';
num_icons--; // *이 줄어든 경우
if(desktop[num_icons] == '.'){ // 원래의 마지막 것이 .이었다면 empty--
num_empty--;
}
}
}
else{ // 안쪽에 있는 경우
if(desktop[index] == '.'){
desktop[index] = '*'; // *이 늘어난 경우.
if(desktop[num_icons] == '.'){ // 추가될 것이 .이면 empty++
num_empty++;
}
num_icons++;
num_empty--; // 원래 있던 empty가 사라졌음
}
else{ // == '*'
desktop[index] = '.';
num_icons--; // *이 줄어든 경우
if(desktop[num_icons] == '.'){ // 원래의 마지막 것이 .이었다면 empty--
num_empty--;
}
num_empty++; // 원래 있던 *이 사라졌음
}
}
cout<<num_empty<<'\n';
}
}코드 중복이 좀 있긴 한데, 모든 logic을 확인하려면 좀 늘려쓰는 게 낫다.
G번
Graph DP + topological sort -> 깨부
'PS > PS Log' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 22.08.22. 풀었던 문제들 (0) | 2022.08.22 |
|---|---|
| 22.08.21. 풀었던 문제들 (0) | 2022.08.22 |
| 22.08.19. 풀었던 문제들 (0) | 2022.08.20 |
| 22.08.18. 풀었던 문제들 (0) | 2022.08.20 |
| 22.08.17. 풀었던 문제들 (0) | 2022.08.20 |
